By Sabri Skhiri
Among the NVIDIA GTC Paris crowd was our CTO Sabri Skhiri, and from quantum computing breakthroughs to the full-stack AI advancements powering industrial digital twins and robotics, there is a lot to share! Explore with Sabri GTC 2025 trends, keynotes, and what it means for businesses looking to innovate.

The Trends
The NVIDIA GTC Paris conference showcased the company’s unprecedented scale and breadth of innovation, cementing its leadership beyond traditional GPU markets. With an exhibition floor spanning thousands of attendees, NVIDIA mapped a vision that extends from quantum computing to autonomous systems, industrial digital twins, advanced robotics, and comprehensive AI safety. Jensen Huang’s keynote underscored how NVIDIA’s end-to-end stack—spanning hardware, software, and cloud services—unlocks synergies across domains, enabling:
- Quantum and Hybrid Computing via the CUDA-Q platform
- Omniverse-Powered Physical Simulation for AV training, robotic manipulation, and digital twins in manufacturing and consumer goods marketing
- Next-Generation Data Centers with the Grace Blackwell architecture and AI factory design
- Agentic and Generative AI using the NeMo Triton (Nemotron) and partnerships (Mistral, Perplexity)
- Global Multi-Cloud AI through DGX Cloud Lepton
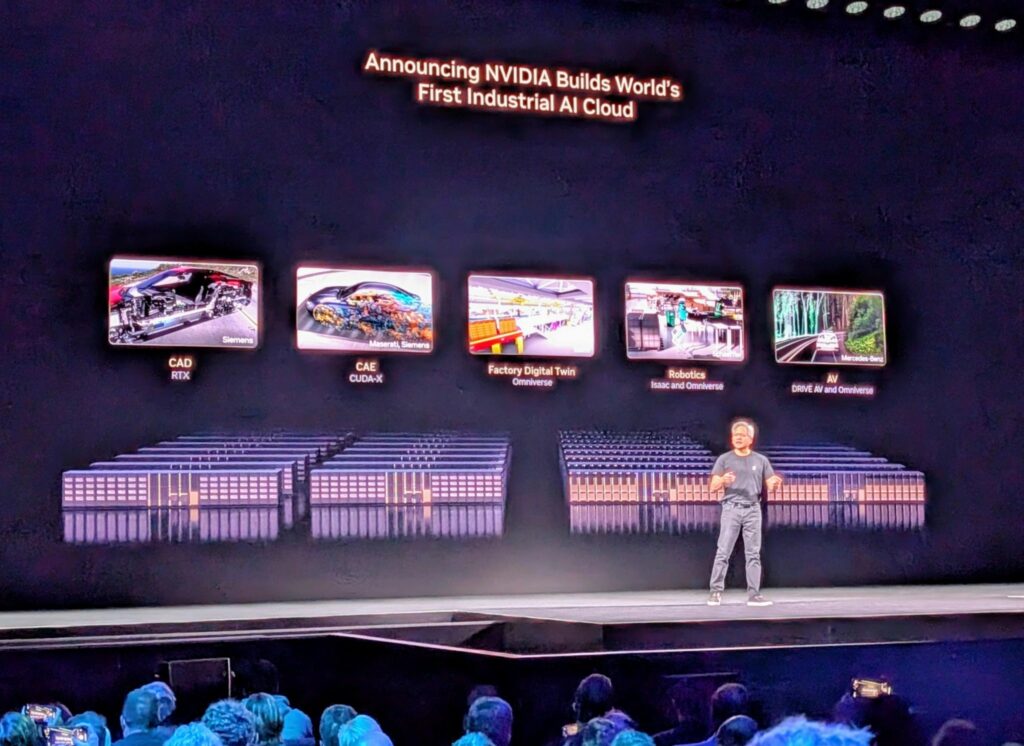
- Industrial AI Clouds anchoring Europe’s first AI factory for manufacturing
- Robotics Platforms with the Newton physics engine and Isaac hardware
- Automotive AI Safety via the HALOS framework and CVPR AV Challenge success
I have also noticed a growing trend: major telecom operators—including Orange, T-Mobile, Telenor, and Swisscom—are positioning themselves as sovereign cloud providers. Through deepening partnerships with NVIDIA and integration into its Cloud Partner Program, they plan to offer the full NVIDIA stack—GPUs, AI software, APIs, and hosting—directly from their own data centers. This strategy aligns closely with the EU’s increasing emphasis on digital sovereignty and regulatory compliance.
NVIDIA’s emphasis at GTC Paris 2025 was not on predicting the future of AI or quantum computing, but rather on the practical application of existing technologies. They showcased their strategy for industrialising these advancements across sectors like manufacturing, automotive, pharmaceuticals, finance, retail, robotics, agriculture, and food. This approach relies on delivering a comprehensive software suite built upon their robust hardware platforms.
The Keynotes
Jensen Huang - The AI vision
Jensen delivered an amazing keynote covering the main trends of the conference.
CUDA-Q & Quantum Computing

CUDA-Q is NVIDIA’s open-source, qubit-agnostic platform enabling hybrid quantum-classical programming. A single CUDA-Q program can orchestrate GPUs, CPUs, and QPUs, providing GPU-accelerated simulation of quantum circuits when hardware is unavailable. This model accelerates error correction and logical qubit management, positioning GPUs as real-time controllers for emerging QPU architectures (see developer.nvidia.com).
Jensen Huang noted that quantum computing has reached an inflection point—shifting from theoretical promise to near-term practical applications—which will tackle problems that even today’s largest AI models struggle to process within reasonable timeframes.
Related success stories:
- CUDA‑Q is live on Denmark’s supercomputer Gefion, enabling researchers to simulate quantum algorithms in fluid dynamics with Ansys and DCAI—accelerating workflows on real-world problems, Link.
- French startup Alice & Bob integrated CUDA‑Q with its Dynamiqs library to speed quantum-state simulations by up to 75×, aiding in fault-tolerant qubit development, Link.
- France’s quantum innovator Pasqal joined forces with NVIDIA, connecting its QPUs to CUDA‑Q for enhanced programming and simulation capabilities, Link.
AI Evolution and Waves
Huang framed AI’s progress in four waves:
- First Wave: Machine Learning
- Second Wave: Generative and Multimodal AI
- Third Wave: Agentic AI (perception → understanding → reasoning → planning → action)
- Fourth Wave: Physical/Robotics AI (motion generation, dynamic adaptation)
What stood out in Paris: European partners (e.g., Siemens, Novo Nordisk, Shell) are now building their own agentic AI agents using NVIDIA’s Blueprints and NeMo Agent toolkit—tailored to regional languages and data sovereignty.
NVIDIA’s new “agentic AI safety” blueprint was also introduced for secure deployment across industries and governments.
Omniverse: “Universe” of Physical Simulation
Omniverse provides a unified platform for realistic physics and behaviour simulation:
- Rigid-body, fluid, and destruction physics via Extensions.
- Digital twins of factories, vehicles, and consumer products using USDPhysics schemas.
- Integration with AI for training AVs in diverse conditions, robotic task adaptation, and real-time marketing visualisation across cultural markets, Link.
Major consumer and luxury brands (L’Oréal, Nestlé, LVMH) showcased digital twins via Omniverse as Nestlé who launched an AI-powered content workflow with Accenture, converting 4,000 products into 3D twins and targeting 10,000 in two years. Interestingly, Nvidia is pushing the concept quite far by even presenting Omniverse as a platform for the fashion and the art industry as described in this post. An entire floor of the conference was dedicated to an Omniverse art gallery.
Grace Blackwell Architecture
NVIDIA’s Blackwell-architecture GPUs (208 billion transistors) manufactured on TSMC’s 4NP process feature dual reticle-limited dies connected by a 10 TB/s interconnect nvidia.com. Combined with Grace CPUs in a Blackwell-Grace module, racks can host nine dual-rail nodes offering 100 TB/s NVLink, liquid cooling, and sub-rack supercomputer scalability—all at approximately $500 K per node. Weekly production of 1,000 such modules fuels AI factories and on-premises supercomputers, from data centres down to laptops and workstations.
- NVIDIA is partnering with European infrastructure leaders (Siemens, Schneider Electric) to build sovereign “AI factories”—complete with scalable cooling and direct-current architectures.
- A pan-European rollout includes new tech centres and sovereign AI hubs in France, Germany, Italy, Finland, the U.K., Spain, Sweden—underscoring regional commitment link.
Generative AI & NeMo/Nemotron
Nemotron is NVIDIA’s family of multimodal models provides state-of-the-art agentic reasoning for graduate-level scientific reasoning, advanced math, coding, instruction following, tool calling, and visual reasoning. They are post-trained on LLaMA and DeepSeek-R1, optimized via neural architecture search, RL, and synthetic data. These models excel at reasoning and agentic tasks, enabling sovereign LLMs deployed on-prem or via NVIDIA Cloud NeMoTron (see doc).
Partnerships announced at GTC:
- Mistral AI: Deploying 18,000 Blackwell GPUs in a new Paris-area facility, ft.com.
- Perplexity: Localizing reasoning models across Europe, generating synthetic data for low-resource languages, and distributing via Perplexity’s platform and DGX Cloud Lepton, reuters.com.
NVIDIA DGX Cloud Lepton
DGX Cloud Lepton offers a “virtual global AI factory,” unifying GPU compute across cloud providers into one developer-friendly platform. Features include:
- Instant access to NVIDIA APIs, serverless endpoints, and Blueprints
- Region-specific GPU resource selection for sovereign AI
- Marketplace integration with NVIDIA Cloud Partners (NCPs)
Lepton simplifies multi-cloud AI deployment, enabling enterprises to prototype in one region and scale globally while adhering to data-governance requirements.
Digital Twins & Industrial AI Cloud (Europe)
NVIDIA announced Europe’s first Industrial AI Cloud, a Germany-based AI factory for real-time design, simulation, wind-tunnel analysis, and factory digital twins. Built on Omniverse, this ecosystem supports manufacturers (e.g., Mercedes-Benz, Bouygues Télécom, BMW) with turnkey digital-twin deployment, driving efficiency and innovation on the shop floor.
This EU AI factory initiative is part of a broader European AI infrastructure push—underscoring sovereignty, local expertise, and strategic autonomy.
AI Robotics: Isaac Newton
Newton is an open-source physics engine co-developed with Google DeepMind and Disney Research, enabling high-fidelity robot learning in virtual environments via NVIDIA Warp.
Coupled with Jetson Thor (AI inference modules) and Omniverse simulation, Newton trains embodied agents—from walking on varied terrains to complex manipulation—before real-world deployment. Disney and DeepMind highlighted Newton’s role in powering robotic effects and research at scale
AI Safety in Automotive: HALOS Framework
NVIDIA’s HALOS is a full-stack safety system for autonomous vehicles, unifying chips (AGX), training (DGX), and simulation (Omniverse/Cosmos) with design-time, deploy-time, and validation guardrails. HALOS includes:
- Curated safety datasets and continuous safety flywheels
- Automated safety evaluations and triage workflows
- Compliance with ISO 26262 ASIL D and ISO/SAE 21434 cybersecurity standards
- Independent TÜV assessments and 240+ AV-safety research papers
In the CVPR Autonomous Grand Challenge, NVIDIA’s end-to-end AV model—trained in Omniverse and validated via HALOS—won top honors for safe, comfortable trajectory planning.
Favourites Talks
AI Safety: From Autonomous Vehicles to Broader Physical AI
Generative AI and large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being integrated into in-cabin AI systems for next-generation vehicles. These models enable natural interaction through multimodal inputs such as voice and image. For instance, a driver could say, “Find a parking spot in the shade,” and the system would interpret and act on this request. In-cabin AI can also be used for driver safety features, such as detecting driver drowsiness or distraction, and in more advanced use cases, it can support autonomous driving decisions.
However, deploying such capabilities requires robust AI safety frameworks. In response to this need, NVIDIA has developed HALOS, an end-to-end AI safety platform that spans the entire lifecycle of an automotive AI system—from model design and training to deployment and real-time monitoring.
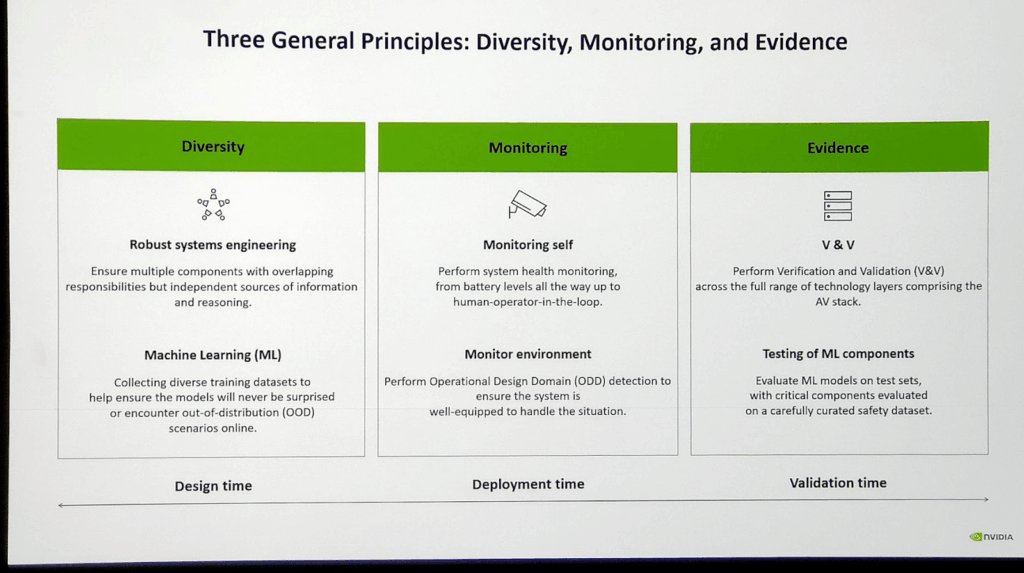
A critical component of this platform is the Omniverse simulation environment. NVIDIA uses Omniverse to recreate high-fidelity, physics-accurate virtual environments where AI models can be trained and validated across a wide range of edge cases, weather conditions, and road scenarios. This virtual training helps ensure the models perform reliably in real-world conditions.
To support these demanding workloads in real-time, NVIDIA offers an automotive-grade hardware stack, effectively a high-performance, embedded version of a gaming workstation. This stack includes GPUs capable of running LLMs and enforcing safety guardrails directly within the vehicle, enabling low-latency decision-making and local AI inference without relying on cloud connectivity.
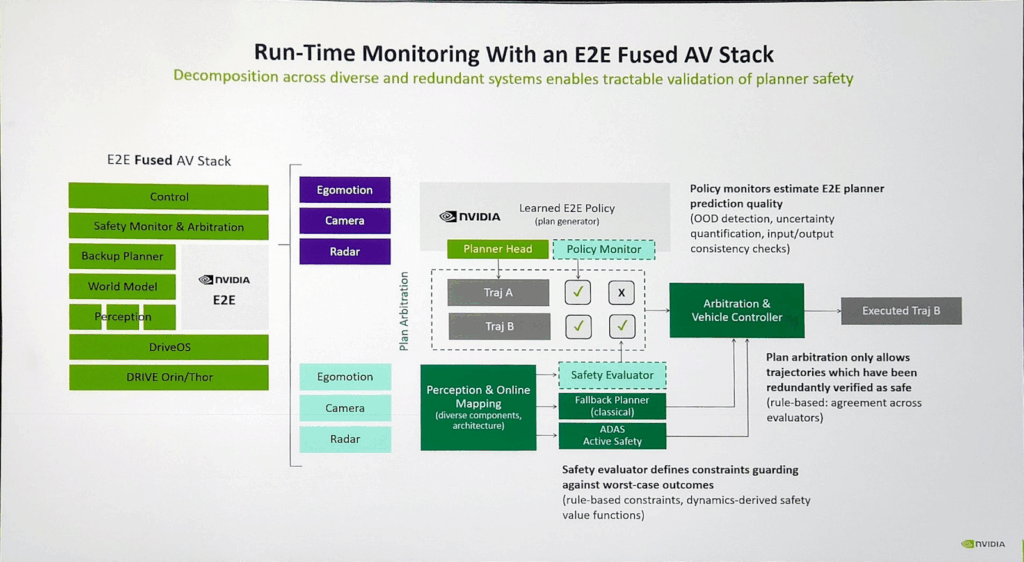
Together, these technologies represent NVIDIA’s vision for safe, intelligent, and autonomous mobility systems. Finally, Wayve introduced their autonomous vehicle model built on an LLM fine-tuned on Nvidia platform.
Generative AI in Automotive
During the expert discussions, I also had the opportunity to explore concrete use cases. The experts introduced the concept of “cabin AI,” referring to all AI systems embedded within the vehicle interior.
The starting point is the idea of embedding a gaming-grade workstation inside the car—engineered to be robust enough to operate reliably for more than 10 years in an automotive environment. This level of computing power enables two major categories of applications: monitoring and user interaction.
1. Monitoring
This includes traditional safety-related features such as:
- Driver attentiveness monitoring (e.g., detecting drowsiness),
- Detecting a child left unattended in the back seat when the doors are locked,
- Lane detection and departure warnings.
2. User Interaction
The second category, however, is even more compelling. It involves embedding a large language model (LLM) connected to the vehicle’s internal APIs. This allows voice-based commands such as: “Open the window,” “Turn on the AC,” “Adjust the seat position,” etc.
The real innovation emerges when this LLM is combined with a vision-language model (VLM) integrated with the vehicle’s cameras. For example, a command like:
“Find me a parking spot near this shop and under the shade of a tree.”
…requires the system to:
- Understand and decompose the natural language instruction,
- Retrieve GPS data and identify the shop’s location,
- Activate the cameras upon approach,
- Analyse the visual scene in real time,
- Detect potential parking spots and assess shading (e.g., based on tree cover or building shadows),
- Reason about depth and spatial orientation to confirm feasibility.
This kind of complex, multimodal interaction is at the core of next-gen cabin AI systems. NVIDIA is currently collaborating with Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and several Chinese car manufacturers to implement and scale these use cases in upcoming vehicle platforms. In conclusion, documenting these interactions will significantly enhance our understanding of driver behaviour, enabling the delivery of more personalised and relevant services.
Accelerating Automotive Innovation with Accelerated Computing, Digital Twins, and AI
BMW described how they transformed their factory floor into a digital twin using 3D scans and imported that model into NVIDIA Omniverse for optimisation and simulation. This setup has unlocked approximately 4,000 use cases, with 35 % ROI and 70 % of factory planning executed virtually to date.
3D Point Clouds & USD File Integration
Omniverse supports importing 3D point clouds—captured from the physical plant—by converting them into USD (Universal Scene Description) format. USD is an open, extensible file format and ecosystem (developed by Pixar, Adobe, Apple, Autodesk, NVIDIA, and others) designed for collaborative 3D scene composition, including geometries, materials, physics, lighting, and animation Link.
These USD files represent both static structures (e.g., walls, machinery) and dynamic elements (e.g., conveyor belts, robotic arms). Once in USD form, Omniverse can efficiently construct a realistic virtual factory environment.

AI Agents & Virtual Factory Interaction
Omniverse enables the integration of AI agents, including those powered by LLMs and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). In demos, users queried the virtual factory to:
- Identify non-connected components,
- Detect missing safety installations, such as ramp railings,
- Perform guided walkthroughs to locate specific assets or risks.
These AI agents can reason directly over the virtual model, helping automate checks and facilitate interactive inspection workflows.
Summary
- Digital twin creation: BMW leveraged 3D scanning and USD to recreate factories in Omniverse.
- Rich USD ecosystem: USD provides a robust, scenegraph-based format for physical and simulated assets Link.
- AI-driven inspection: Integrated LLM- and RAG-powered agents allow natural-language queries and automatic detection of design or safety issues based on the virtual model.
